How to find affordable long term care insurance options for seniors – How to find affordable long-term care insurance options for seniors? It’s a question weighing heavily on the minds of many families. Planning for the future, especially when it comes to potential health issues and the associated costs, can feel overwhelming. But fear not! Navigating the world of long-term care insurance doesn’t have to be a daunting task.
This guide breaks down the essentials, helping you find affordable options that offer peace of mind for you and your loved ones.
We’ll explore various insurance policies, government assistance programs, and financial strategies to help you create a comprehensive plan. From understanding the different levels of care available to learning how to compare providers, we’ll equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions. Remember, proactive planning is key to securing a comfortable and financially responsible future. Let’s dive in and discover how you can secure your golden years without breaking the bank.
Understanding Long-Term Care Needs of Seniors

Planning for long-term care is a crucial aspect of senior life, often overlooked until a crisis arises. Understanding the various care options and the factors influencing the need for them empowers seniors and their families to make informed decisions and proactively address potential future challenges. This section will explore the different types of long-term care, the factors contributing to the need for it, and provide examples to illustrate the importance of planning ahead.
Types of Long-Term Care Services
Long-term care encompasses a wide range of services designed to assist seniors with daily living activities. These services are tailored to individual needs and can range from minimal support to comprehensive, 24-hour care. The specific type of care required depends on the individual’s physical and cognitive abilities, as well as their financial resources.
Factors Influencing the Need for Long-Term Care, How to find affordable long term care insurance options for seniors
Several factors significantly influence a senior’s need for long-term care. Age, of course, plays a major role, with the likelihood of needing assistance increasing with age. Pre-existing health conditions, such as dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, or arthritis, significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks independently and necessitate varying levels of care. Lifestyle choices, such as maintaining an active lifestyle and a healthy diet, can also influence the onset and severity of age-related health issues, indirectly impacting the need for long-term care.
A family history of specific health conditions can also be a predictive factor.
Scenarios Requiring Long-Term Care
Consider these scenarios: A 78-year-old with Alzheimer’s disease gradually loses the ability to manage personal hygiene and household tasks. A 65-year-old recovering from a stroke requires physical therapy and assistance with mobility. An 85-year-old with severe arthritis finds it increasingly difficult to perform simple chores like cooking and cleaning. These situations highlight the diverse circumstances where long-term care becomes essential.
Navigating the world of long-term care insurance for seniors can be tricky, especially when budgets are tight. Finding affordable options often involves comparing plans and exploring government assistance programs. However, planning for the future also involves considering other insurance needs; for example, young adults should also explore their options, perhaps checking out resources like this article on what are the best life insurance policies for young adults with low income to understand their own financial security.
Ultimately, securing affordable long-term care insurance requires careful research and planning, regardless of age.
In each case, the level and type of care needed would vary depending on the individual’s specific needs and capabilities.
Comparison of Long-Term Care Options and Costs
The cost of long-term care varies significantly depending on the level of care required and geographic location. The following table provides a general comparison, keeping in mind that actual costs can fluctuate widely:
| Level of Care | Description | Services Provided | Estimated Monthly Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Care | Care provided in the senior’s home | Assistance with bathing, dressing, meal preparation, medication reminders, light housekeeping | $4,000 – $7,000 |
| Assisted Living | Residential setting with supportive services | Assistance with daily living, meals, medication management, social activities, some medical oversight | $4,500 – $8,000 |
| Nursing Home (Skilled Nursing Facility) | 24-hour medical care in a facility | Skilled nursing care, medical treatments, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy | $8,000 – $12,000+ |
| Nursing Home (Intermediate Care) | 24-hour care with less intensive medical needs | Assistance with daily living, medication management, some medical monitoring | $6,000 – $10,000 |
*Note: These cost estimates are averages and can vary significantly based on location, the level of care needed, and the specific services provided. It’s crucial to obtain personalized cost estimates from providers in your area.*
Exploring Affordable Long-Term Care Insurance Options
Securing your future and ensuring access to quality long-term care doesn’t have to break the bank. Understanding the various types of long-term care insurance and how their features impact cost is crucial for making an informed decision. This section will delve into the different policy options available, exploring ways to find affordable coverage that meets your specific needs.
Types of Long-Term Care Insurance Policies
Several types of long-term care insurance policies cater to diverse needs and budgets. Choosing the right one depends heavily on your individual circumstances and risk tolerance. The most common types include traditional, hybrid, and partnership policies. Traditional policies offer straightforward coverage for long-term care services, while hybrid policies combine long-term care benefits with life insurance. Partnership policies offer additional benefits through state-sponsored programs.
Comparing Policy Features and Affordability
Traditional long-term care insurance policies typically offer the most comprehensive coverage, but they often come with higher premiums. The benefit period (length of time coverage is provided) and daily benefit amount significantly influence the cost. A shorter benefit period or lower daily benefit amount can lead to lower premiums. Hybrid policies, combining life insurance and long-term care, can be a more affordable option for some, as the life insurance component offers a death benefit even if long-term care benefits are not used.
Partnership policies can provide cost savings through state subsidies and tax advantages, but eligibility requirements vary by state. The key is to carefully weigh the coverage offered against the premium cost to find the best balance for your financial situation.
Factors Affecting Long-Term Care Insurance Premiums
Several factors contribute to the cost of long-term care insurance premiums. Your age is a major determinant, with younger individuals generally receiving lower premiums than older applicants. Your health status also plays a significant role, as individuals with pre-existing conditions may face higher premiums or even be denied coverage. The policy’s benefit structure, including the benefit period, daily benefit amount, and inflation protection, directly affects the cost.
Higher benefits naturally translate to higher premiums. Finally, the insurer’s financial strength and reputation can also influence pricing.
Reducing the Cost of Long-Term Care Insurance
There are strategies to make long-term care insurance more affordable. Opting for a shorter benefit period, for example, can significantly reduce premiums. Similarly, choosing a higher deductible means lower monthly payments, although it means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket before coverage kicks in. Consider carefully whether you need inflation protection; while beneficial, it increases the cost. Exploring policies with waiting periods can also lower premiums, but this means delaying coverage if you need it.
It’s crucial to balance these cost-saving measures with your individual needs and risk tolerance. For instance, someone with a family history of Alzheimer’s disease might prioritize a longer benefit period, even if it means higher premiums.
Government Assistance Programs and Resources: How To Find Affordable Long Term Care Insurance Options For Seniors
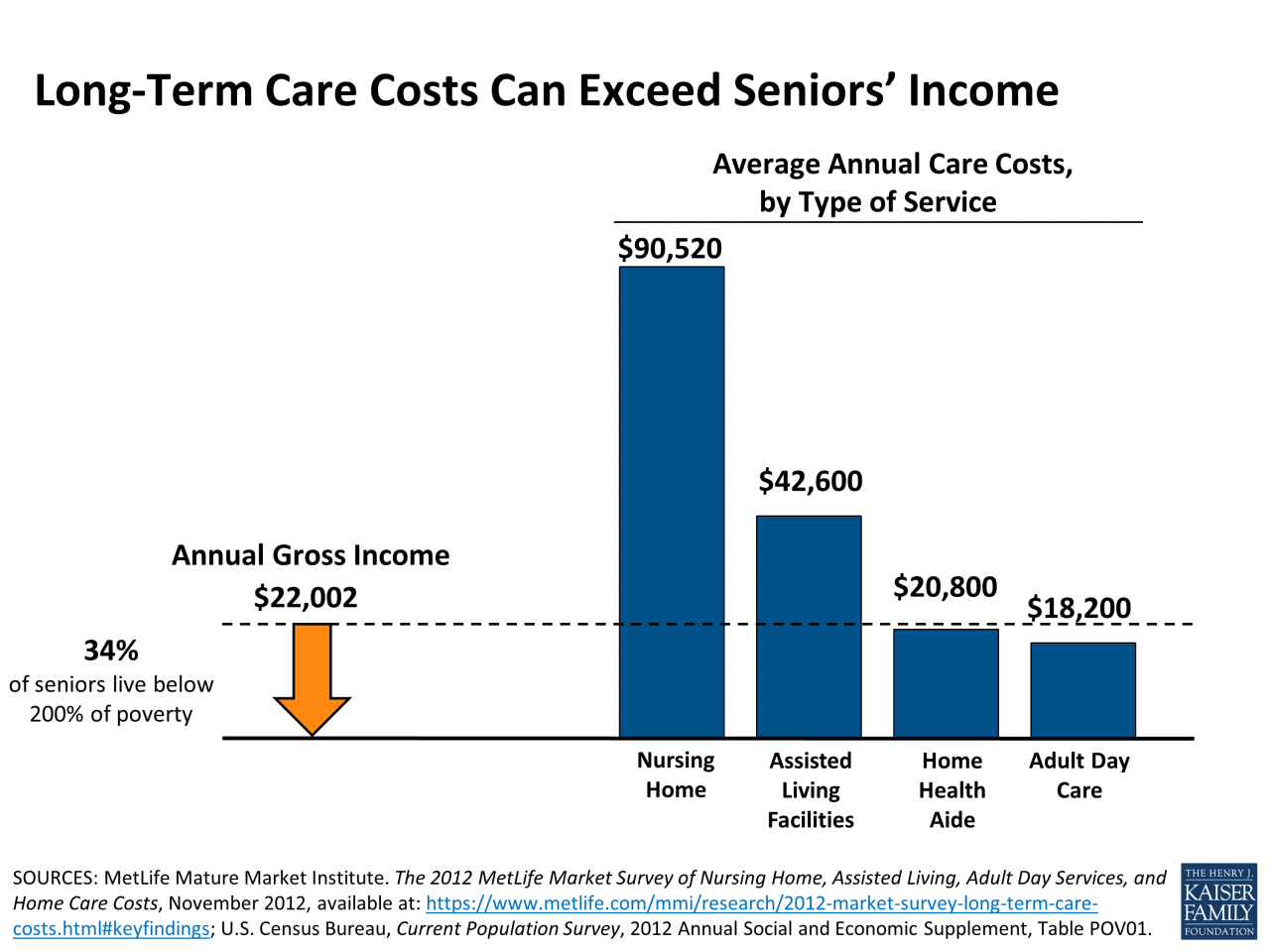
Navigating the complexities of long-term care costs can be daunting, especially for seniors on a fixed income. Fortunately, several government programs are designed to offer financial assistance and support. Understanding these programs, their eligibility criteria, and limitations is crucial for securing the best possible care while managing expenses effectively. This section will delve into the key government resources available to seniors facing long-term care needs.
Medicaid and Medicare: Key Differences and Eligibility
Medicaid and Medicare are two distinct federal government programs that can assist with long-term care expenses, but they operate under different eligibility rules and cover different aspects of care. Medicare, primarily focused on short-term medical care, offers limited coverage for long-term care, mainly in the form of skilled nursing facility care following a hospital stay. Medicaid, on the other hand, is a means-tested program designed to provide comprehensive medical and long-term care services to low-income individuals and families.
Eligibility for both programs varies by state.
- Medicare: Primarily covers short-term rehabilitation and skilled nursing care after a hospital stay. It does not cover custodial care (assistance with activities of daily living like bathing and dressing), which constitutes the majority of long-term care needs. Eligibility is based primarily on age (65 or older) and work history.
- Medicaid: Covers a broader range of long-term care services, including nursing home care, home healthcare, and assisted living (depending on state regulations). Eligibility is determined by income and asset limits, which are significantly lower than Medicare’s requirements. The application process involves submitting extensive documentation of income, assets, and medical history.
Application Processes and Challenges
Applying for Medicaid can be a complex and time-consuming process. Applicants must provide extensive documentation to demonstrate their financial eligibility, including bank statements, tax returns, and proof of income and assets. The process can be further complicated by varying state regulations and requirements. For example, some states have stricter asset limits than others, while others may have waiting lists for certain services.
Navigating the bureaucratic hurdles can be overwhelming for seniors and their families, often requiring assistance from social workers or elder law attorneys. Furthermore, the stringent eligibility criteria can exclude many seniors who need long-term care but do not meet the strict income and asset thresholds.
Comparing Benefits and Limitations of Government Assistance Programs
The table below summarizes the key benefits and limitations of Medicaid and Medicare in the context of long-term care:
| Program | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Medicare | Covers short-term skilled nursing care after hospitalization; relatively easy to qualify for if eligible for age and work history. | Limited coverage for long-term care; does not cover custodial care; significant out-of-pocket costs can still apply. |
| Medicaid | Covers a wide range of long-term care services, including nursing home care and home healthcare; potentially covers a substantial portion of long-term care costs. | Strict income and asset limits; complex application process; significant documentation required; long waiting lists possible in some states; may require spending down assets to qualify. |
Planning and Financial Strategies for Long-Term Care

Planning for long-term care is crucial, as the costs can be substantial and unpredictable. A proactive approach, combining careful financial planning with a realistic understanding of potential needs, is essential to ensure a secure future. This involves assessing your current financial situation, exploring available resources, and implementing strategies to mitigate the financial burden of long-term care.
Step-by-Step Guide to Planning for Long-Term Care Costs
Effective planning requires a structured approach. This step-by-step guide provides a framework for navigating the process:
- Assess your current financial situation: Begin by evaluating your assets, including savings, investments, and retirement accounts. Calculate your monthly income and expenses to determine your financial capacity.
- Estimate long-term care costs: Research the average cost of long-term care in your area. Consider the type of care you might need (home care, assisted living, nursing home) and the potential duration of care. Online resources and local agencies can provide cost estimates.
- Explore long-term care insurance options: Determine if purchasing a long-term care insurance policy is feasible given your budget and health status. Compare policies from different insurers, paying close attention to coverage limits, premiums, and benefit periods.
- Develop a long-term care budget: Create a realistic budget that incorporates projected long-term care expenses. Factor in potential inflation and changes in your health needs. Regularly review and adjust your budget as circumstances change.
- Implement financial strategies: Explore various financial strategies to help fund long-term care, such as reverse mortgages or long-term care partnerships. Consult with a financial advisor to determine the most suitable options for your situation.
- Review and update your plan: Regularly review your long-term care plan, updating it as your circumstances or health status changes. Consider seeking professional advice from financial planners and elder law attorneys.
Examples of Financial Strategies for Long-Term Care
Several financial strategies can help seniors manage the costs of long-term care. These strategies require careful consideration and professional advice.
Navigating the world of senior care insurance can be tricky, requiring careful comparison of policies and providers to secure affordable long-term care. Just like understanding the fine print is crucial when choosing a policy, remember to also be aware of potential pitfalls; for example, check out this article on what are the hidden fees and charges in car insurance policies to see how unexpected costs can arise.
This awareness helps you approach long-term care insurance with a more informed and financially savvy perspective, ensuring you get the best value for your money.
- Reverse Mortgages: A reverse mortgage allows homeowners aged 62 or older to access the equity in their home without selling it. The loan is repaid upon the homeowner’s death or sale of the home. However, it’s crucial to understand the terms and conditions carefully, as interest accrues over time.
- Long-Term Care Partnerships: These programs, offered in some states, coordinate with Medicaid to help cover long-term care costs. The programs typically require individuals to spend down a certain amount of assets before becoming eligible for Medicaid benefits. The specific requirements vary by state.
- Life Insurance Policies with Long-Term Care Riders: Some life insurance policies offer riders that provide long-term care benefits. These riders allow a portion of the death benefit to be used to pay for long-term care expenses while the policyholder is still alive. This can be a valuable option for those who qualify.
Creating a Realistic Budget Incorporating Long-Term Care Expenses
Creating a realistic budget requires careful consideration of both current and future expenses. It’s essential to account for potential increases in healthcare costs due to inflation. For example, if a senior anticipates needing assisted living for five years, they should research current costs and factor in a reasonable annual inflation rate (e.g., 3-5%) to project total expenses. This ensures that the budget accurately reflects the potential financial burden.
Unexpected medical emergencies should also be considered and accounted for through an emergency fund or other financial reserves.
Tips for Maximizing the Effectiveness of Financial Planning for Long-Term Care
Effective financial planning requires proactive steps and professional guidance.
- Consult with a financial advisor: A financial advisor can help you assess your financial situation, develop a comprehensive plan, and explore various financial strategies tailored to your needs.
- Consider estate planning: Proper estate planning, including wills and trusts, can help protect your assets and ensure your wishes are carried out.
- Stay informed about government assistance programs: Keep abreast of changes in government assistance programs that may impact your eligibility for long-term care benefits.
- Maintain good health: Maintaining good health can help reduce the need for extensive long-term care, minimizing the associated costs.
Finding and Evaluating Long-Term Care Providers

Securing the right long-term care provider is a crucial step in ensuring a senior’s well-being and quality of life. This involves more than just finding a facility; it requires careful research, thorough assessment, and a clear understanding of your loved one’s needs and preferences. Making an informed decision can significantly impact their comfort, health, and overall happiness during this important phase of life.The process of finding and evaluating long-term care providers involves a systematic approach, blending online research with in-person visits and careful consideration of various factors.
This careful vetting ensures that the chosen provider aligns with the individual’s specific needs and the family’s expectations.
Researching and Selecting Reputable Long-Term Care Providers
Begin by utilizing online resources such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) website. This site provides valuable information on nursing homes, including inspection reports, staffing levels, and overall quality ratings. Additionally, seeking recommendations from family, friends, or healthcare professionals can provide valuable insights and personal experiences. Online review sites, while offering a range of opinions, should be considered alongside other research methods for a well-rounded perspective.
Remember to verify the information found online with the provider directly.
Importance of Facility Visits and Assessments
Visiting potential facilities in person is paramount. This allows for a firsthand assessment of the environment, staff interactions, and overall atmosphere. Observe the cleanliness and safety of the facility, paying attention to details such as the residents’ appearance and demeanor. Engage in conversations with staff and residents to gauge the level of care and interaction. A positive and welcoming environment, coupled with attentive and caring staff, suggests a higher quality of care.
Consider visiting at different times of the day to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the facility’s daily operations.
Key Factors in Comparing Long-Term Care Providers
Several key factors must be weighed when comparing providers. Cost is a significant consideration, encompassing not only the basic fees but also additional charges for services such as medication management or specialized care. Quality of care, as measured by CMS ratings and personal observations, is equally important. The staff-to-resident ratio provides insight into the level of attention each resident receives.
Consider the provider’s location and accessibility for family members, as regular visits are crucial for maintaining connection and monitoring care. Finally, examine the provider’s amenities and activities to ensure they align with the resident’s interests and preferences. For example, a facility offering specialized dementia care would be more suitable for a resident with Alzheimer’s disease than a general care facility.
Checklist of Questions for Potential Long-Term Care Providers
Before making a decision, it is vital to ask potential providers specific questions to ensure they meet your needs and expectations.
- What types of care services are offered?
- What is the daily/monthly cost, and what services are included in that cost?
- What is the staff-to-resident ratio?
- What are the qualifications and experience levels of the staff?
- What is the facility’s policy on medication management?
- What are the procedures for handling emergencies and resident safety?
- What activities and programs are available for residents?
- What is the facility’s policy on visitors?
- What is the process for addressing resident complaints or concerns?
- Can I see the most recent inspection report and quality ratings?
Illustrating Long-Term Care Scenarios and Costs

Navigating the complexities of long-term care can be daunting, especially when considering the significant financial implications. Understanding potential scenarios and associated costs is crucial for effective planning. This section illustrates a typical scenario, details the features of a long-term care facility, and explores the potential financial and emotional impact on seniors and their families.
A Senior’s Long-Term Care Scenario and Associated Costs
Let’s consider Mrs. Eleanor Vance, a 78-year-old widow who recently experienced a stroke, leaving her with limited mobility and requiring assistance with daily living activities. Before her stroke, Mrs. Vance lived independently in her home. Post-stroke, her needs escalated rapidly.
Initially, she required in-home care, costing approximately $5,000 per month for a certified nursing assistant to provide assistance with bathing, dressing, and meal preparation. After six months, her needs intensified, necessitating a move to a skilled nursing facility. The cost of this care soared to $10,000 per month, covering 24-hour nursing care, medication management, and physical therapy. If her condition further deteriorates, a move to a more specialized memory care unit might be necessary, pushing monthly costs to potentially $12,000 or more.
These costs don’t include additional expenses such as medication, medical supplies, and transportation.
Description of a Typical Long-Term Care Facility
A typical long-term care facility, such as a skilled nursing facility, often resembles a large residential building. It’s designed with multiple wings or floors, each containing several private or semi-private rooms. The rooms are generally modest in size, furnished with a bed, bedside table, dresser, and chair. Common areas include a spacious lounge with comfortable seating, a dining room for communal meals, and perhaps a recreation area with activities such as puzzles, board games, and television.
Many facilities also have outdoor spaces, such as patios or gardens, for residents to enjoy fresh air and sunshine. The atmosphere aims for a balance between safety and comfort, with features like call buttons in each room and handrails in hallways. While facilities vary, a general feeling of community and support is usually cultivated. Therapeutic services, such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy, are often provided on-site.
Financial Impact of Long-Term Care
The substantial cost of long-term care can significantly deplete a senior’s savings and assets. For Mrs. Vance, even with some supplemental insurance, her savings could be exhausted within a few years, depending on the extent and duration of her care. This can lead to the need for family members to contribute financially, creating considerable strain on their own resources and potentially delaying their own financial goals, such as retirement or children’s education.
Medicaid, a government assistance program, may become a necessary resource to cover the cost of care, but qualification has stringent requirements.
Emotional and Psychological Aspects of Transitioning to Long-Term Care
The transition to long-term care can be emotionally challenging for seniors. Leaving their homes and familiar surroundings can trigger feelings of loss, grief, and isolation. The loss of independence and control over daily life can also lead to feelings of helplessness and depression. Furthermore, adapting to a new environment and routines requires significant adjustment, and social interaction might be different than what the senior is used to.
Family support and professional counseling can play vital roles in helping seniors navigate these emotional and psychological challenges, fostering a smoother transition and improved well-being.